This is because the number of protons the nuclear charge and the number of electrons increases by one every time you go an element to the rightThe elements in a period all have the same number of shells so the shielding effect is the same. This is because the number of protons the nuclear charge and the number of electrons increases by one every time you go an element to the rightThe elements in a period all have the same number of shells so the shielding effect is the same.

Atomic Radius Chart Google Search Chemistry Ionization Energy Periodic Table
Metallic radii for Na Mg and Al.
. What is the trend in atomic radius of the elements across Period 3 and why does this occur. Nuclear charge increases across the period therefore the attraction between the positively charged nucleus and. Decreases from phosphorus to sulfur then increases again.
F electronegativity increases excluding argon g. Table shows the changes in the proton numbers and number of valence electrons when going across Period 2Element in. The atomic radius of the elements decreases from sodium to argon.
The first ionisation energy generally increases across period 3. A atomic number and therefore charge on the nucleus nuclear or core charge increases. This is because the first ionisation energy.
Created by JayWatch the next lesson. Moving across Period 3 the number of protons in the nucleus increases - for example sodium has 11 protons and chlorine has 17 protons. Explain the trend in atomic radius of elements across period 3.
Atomic radius across period 3. This is because the number of protons increases sodium has 11 argon has 18 so the nuclear charge increases. The atomic radius of an atom is the distance from the atoms nucleus to its outermost electron.
The Periodic Table consists of seven periods from Period 1 to Period 7. The graph shows how the first ionisation energy varies across period 3. Terms in this set 12 Trend in atomic radius across the period.
As the atomic number increases the atomic radius decreases. - The atomic radii of period 3 elements decrease across the period. Across the period the atomic radii decrease.
The diagram shows how the atomic radius changes as you go across Period 3. Reason for trend in atomic radius. By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your.
However the trend needs a more detailed consideration than the trend in group 2. - For the same number of energy levels the number of protons in the nucleus increases across the period. The trend of atomic and ionic radii.
What is the trend in atomic radius of the elements across Period 3 and why does this occur. Therefore the attraction between the positive nucleus and negative electrons. Start studying Periodicity- trends across period 3.
You have to ignore the noble gas at the end of each period. This means that as you go across the period the nucleus attracts the electrons more. This leads to the increase in nuclear charge while the shielding effect remains the same hence decrease in atomic radius across.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Lets look at the radii of the simple ions formed by elements as you go across Period 3 of the. Covalent radii for Si P S and Cl.
How many periods are in the periodic tableEach horizontal row of elements in the Periodic Table is known as a period. This is because while the number of electrons increases down the period they only add to the same main energy level and therefore do not. The alkali metals at the extreme left.
How atomic radius is defined and trends across a period and down a group. The increase in nuclear charge attracts the electrons more strongly pulling them closer to. B number of valence electrons increases.
Trends in atomic radius across periods. The atomic radius of the elements decreases from sodium to argon. Across the period the atomic radii decrease.
The graph shows how atomic radius varies across period 3. D first ionisation energy increases. For example Sodium in period 3 has an atomic radius of 186 x10-12 m and chlorine in.
Because neon and argon dont form bonds you can only measure their van der Waals radius - a case where the atom is pretty well unsquashed. There are many trends on the periodic table. This means that as you go across the period the nucleus attracts the electrons more.
JavaScript chart by amCharts 32115. Atomic radius of period 3 elements Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Period 3 element 008 010 012 014 016 018 020 Atomic radius nm. The following general trends are observed as you go across period 3 from left to right.
For example ionization energy electronegativity and of course atomic radius which we will discuss now. This is because the number of protons increases sodium has 11 argon has 18 so the nuclear charge increases. The figures used to construct this diagram are based on.
The atomic and ionic radii in group 1 increases and is very much so close to the trendline considering down the group there is an increase in inner shell electrons which means that there will be a decrease in effective nuclear charge and increase in the shielding effect thus going down the group the elements will have an easier way of losing electrons. Atomic radius decreases across a period because valence electrons are being added to the same energy level at the same time the nucleus is increasing in protons. C atomic radius decreases.
The van der Waals radius for Ar. Variation of Atomic Radii in the Periodic Table Variation Within a Period The Covalent and Van der Waals radii decrease with increase in atomic number as we move from left to right in a period. Across a period atomic radii decrease.
Across a period the atomic radius decreases as the number of protons in the nucleus increases this means the nucleus has a higher nuclear charge and can attract electrons more closely due to the attraction of the positive protons to the negative electrons. Click to see full answer. Answer 1 of 2.
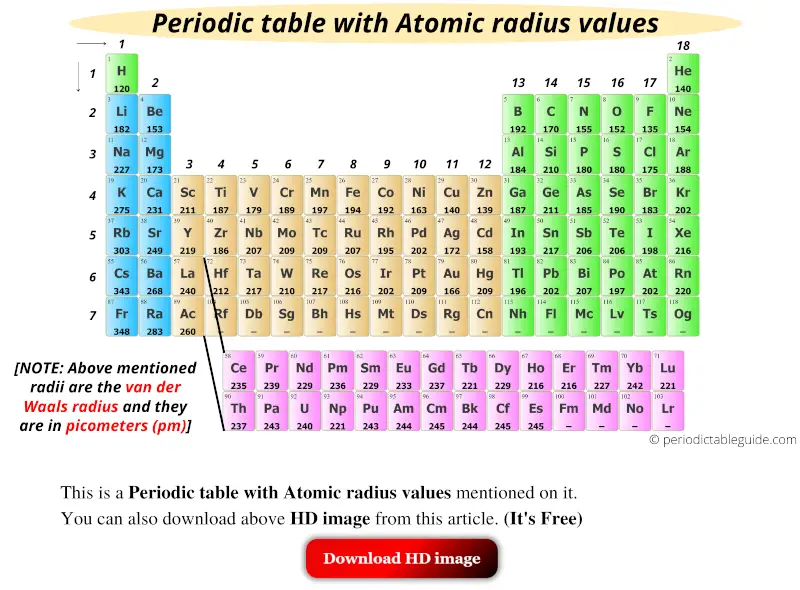
Get The Periodic Table With Atomic Radius Values Img Chart

Periodic Trends And Atomic Radius Chad S Prep

Periodic Table With Relative Atomic Masses Relative Atomic Mass Periodic Table Periodic Chart

Periodic Table Trends Chart Vector Illustration Scheme Stock Vector Illustration Of Graphic Che Amazing Science Experiments Chemistry Lessons Study Biology

Trends Of Period 3 Elements Atomic Radius 2 1 2 Aqa A Level Chemistry Revision Notes 2017 Save My Exams

Atomic Radius Definition Formula Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Are The Periodic Trends For Atomic Radii Ionization Energy And Electron Affinity Socratic

Intro To The Periodic Table Groups And Periods Notes And Worksheets Periodic Table Science Notes School Study Tips

Periodic Trends Variation In Atomic Radii Of Elements In Different Blocks Chemistry Stack Exchange

Suka Chemistry Atomic Radius Trends On Periodic Table

Neon S Melting Point Is 248 67 C Melting Point Boiling Point Atomic Number

Periodic Trends Definition And Properties

A Level Gce Period 3 Element Trends In 1st Ionisation Energy Atomic Radius Pauling Electronegativity Melting Point Boiling Point Electrical Conductivity Density Trends Graphs Plots Discussed Explained Ks5 Revision Notes

Trends Of Period 3 Elements Atomic Radius 2 1 2 Aqa A Level Chemistry Revision Notes 2017 Save My Exams

The Size Of Atom Decreases Across A Period From Left To Right Description From Streamscience Blogspot Com I Searched For This On Bing Com Images พ นธะเคม
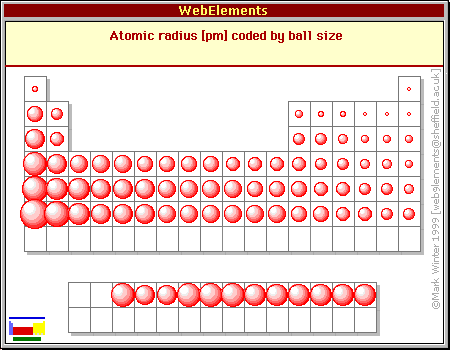
How Does Atomic Radius Change From Left To Right Across A Period In The Periodic Table Socratic

Atomic Radius Study Guide Inspirit

Trends In The Periodic Table Chpt 7 1 Atomic Radius Size 2 Ionization Energy 3 Electronegativity The Ionization Energy Periodic Table Covalent Bonding
